¶ Aromatic substitution
¶ Electrophilic Substitution
Aromatic compounds do not want to participate in addition reactions as doing so will break the conjugation and take away their stability
- However, it is able to undergo reactions such as substitution, and will aim to restore its aromaticity
¶ Electrophilic aromatic substitution
It is the main mode of reactivity of aromatic compounds
The identity of the electrophile is specific to each type of reaction the aromatic compound undergoes (in some cases, we have to generate the electrophiles during the reaction)
¶ Mechanism
When aromatic compounds react with electrophiles, they generally do so through the SEAr mechanism
- The reaction has a two-step mechanism and the first step is rate determining step
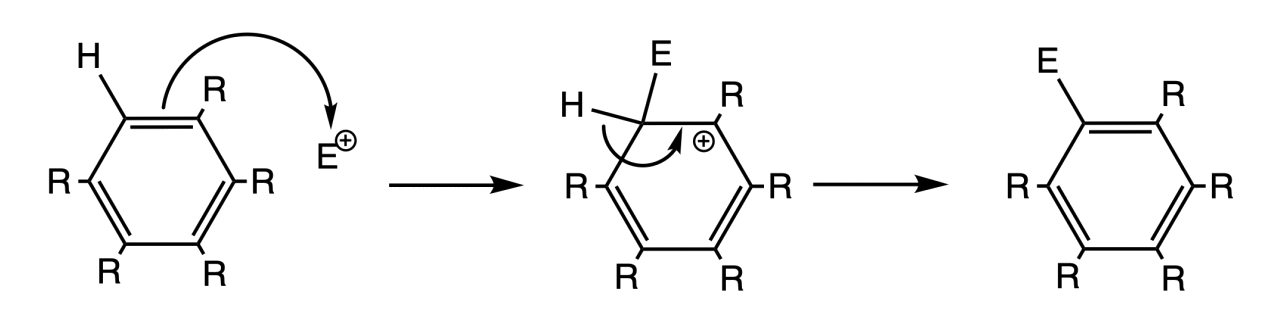
The carbocation intermediate is stabilized through resonance.
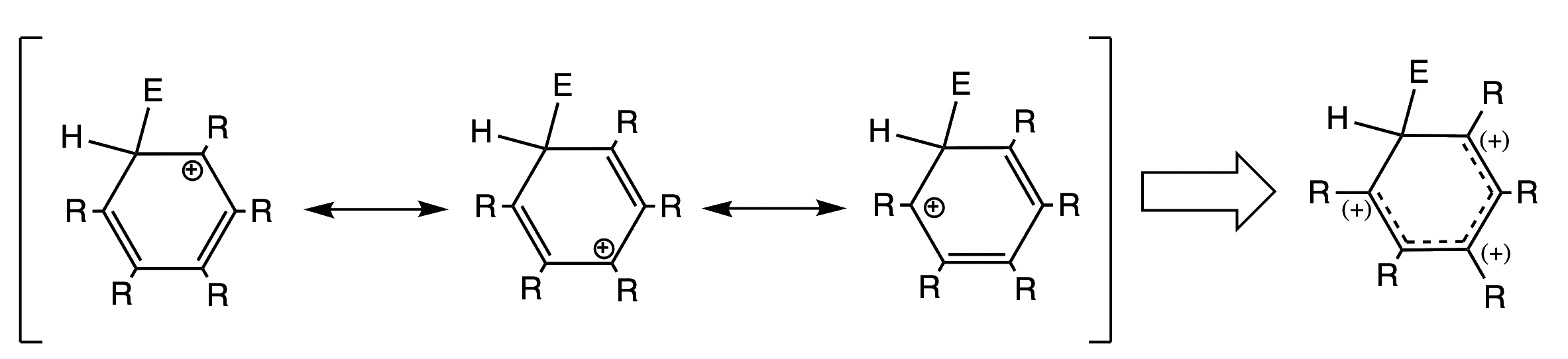
- It is important to notice that even though the positive charge is delocalised, the intermediate is not aromatic due to the fact that the carbon bonded to the electrophile is sp3 hybridised (and the ring is not fully planar)
¶ Ipso-Substitution
The electrophiles are able to attack substituted carbons rather than just hydrogen-bearing carbons
Attack of substituted (ipso) or (1-...) positioned carbon evidently does occur, but they do not lead directly to the substituted products
- This is because de-substitiutation is not a thing, unlike deprotonation
-
Instead, the electrophile changes position to the neighboring ring carbon until it lands on a hydrogen-bearing carbon such that deprotonation can occur
- The way the electrophile changes position is like a carbocation rearrangement
¶ Effects of Substituents
Since the aromatic compound acts as the nucleophile in these reactions, substituents that increases the nucleophilicity of the molecule increases the rate of reaction
- If the substituent is an electron-withdrawing group (EWG) -> rate of reaction will decrease
- if the substituent is an electron-donating group (EDG) -> rate of reaction will increase
Substituents that decrease the rate of reaction relative to an unsubstituted ring are called Deactivating groups, while substituents that increase the rate of reaction relative to an unsubstituted ring are called Activating groups
Electron donating and withdrawing effects originate from a combination of inductive and conjugation / resonance effects
- Inductive effects
The substituent acts as a σ (orbital) donor or acceptor - Conjugation / resonance effects
The substituent donates or withdraws a lone pair / acts as a π donor or acceptor
¶ Regioselectivity
In the absence of substituents, the electrophile can be attached to any position on the aromatic ring, as all positions are equivalent.
- When there are substituent(s) attached to the ring, certain positions relative to the substituent are favoured (i.e. regioselectivity)
- Electrophilic aromatic substitutions are regioselective in the presence of substituents
We can determine which positions are favoured by examining the carbocation intermediate of each position
- When the electrophile is ortho (in 2 & 6 carbon positions) with respect to the substituents